Power
The word “power” is most often associated with electricity in everyday use, but this is not the case in physics.- Power is the rate at which work is done.
- This means that power measures how quickly energy is being used.
- Since it is the rate at which something is happening, time must be involved somehow.
- If you look at the basic formula for power, you’ll see that it is the same as many formulas that involve time.
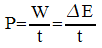
P = power (Watts)
W = Δ E = work (Joules)
t = time (seconds)
W = Δ E = work (Joules)
t = time (seconds)
Sometimes you will see Δ E instead of W in the above formula.
- Δ E just means change in energy, which is what work is all about.
- In honour of his search for a more efficient engine (which was better at converting energy!), the unit for power is called the Watt after James Watt.
- Think of a light bulb… you always talk about how many Watts the bulb is, like a 60 W bulb.
- That just means that the light bulb is using 60 Joules of energy every second.
| Switch to Index |
 Energy Skate Park: Basics |
 Generator |
 Faraday's Electromagnetic Lab |
||
 Masses & Springs |
 My Solar System |
 Energy Skate Park |
||
 Gas Properties |
 Balloons & Buoyancy |
 States of Matter |
||
 Nuclear Fission |
 The Ramp |
No comments:
Post a Comment